Solder paste is important in making electronic devices. It is a mixture of suspended powder in a flux medium and tiny metal balls. When soldering parts to printed circuit boards, it is required. Solder paste ensures there’s top accuracy and precision.
There are various means of applying the paste onto a printed circuit board. Some of the most preferred methods include jet printing, stencil printing, and screen printing. After the application of the paste onto the PCB, heat is introduced to melt the metal balls into a strong bond.
We have created this solder paste and accompanying usage guidelines to help you secure solid couplings and a well-functioning PCB. Read to understand more.

Tiny metallic solder flakes are combined with a flux binder to create a solder paste. This paste is then used on PCB pads to attach components. Heating is used throughout the soldering process, causing the solder to break down and move, forming a strong connection that holds the parts to the PCB. Surface Mount Technology assembly procedures often involve the application of solder paste by assemblers.
There are many applications for solder paste in the electronics sector. It connects printed circuit boards (PCBs) and parts for electronics. The paste is applied to the PCB pads where the individual parts are located. Components thereafter are placed on the paste.
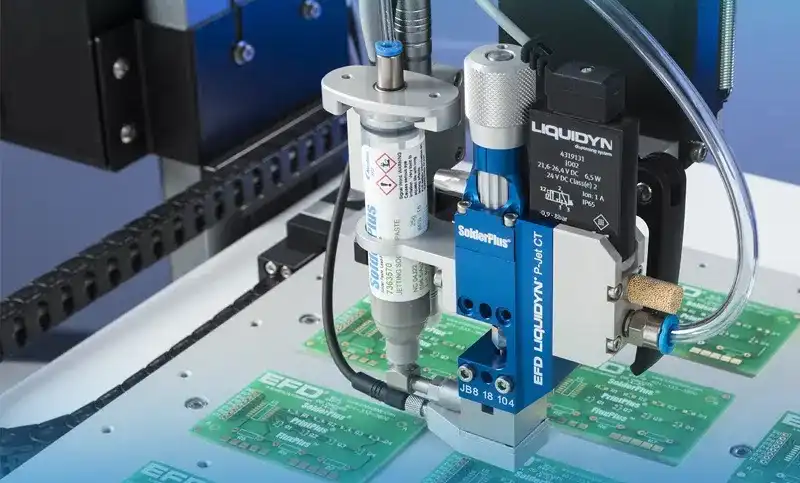
Frequently, a stencil is utilized for applying solder paste. It is placed over the PCB and paste spread over the openings in the stencil. In this kind of method, a syringe may also be employed. Other dispensing equipment can also serve a similar purpose.
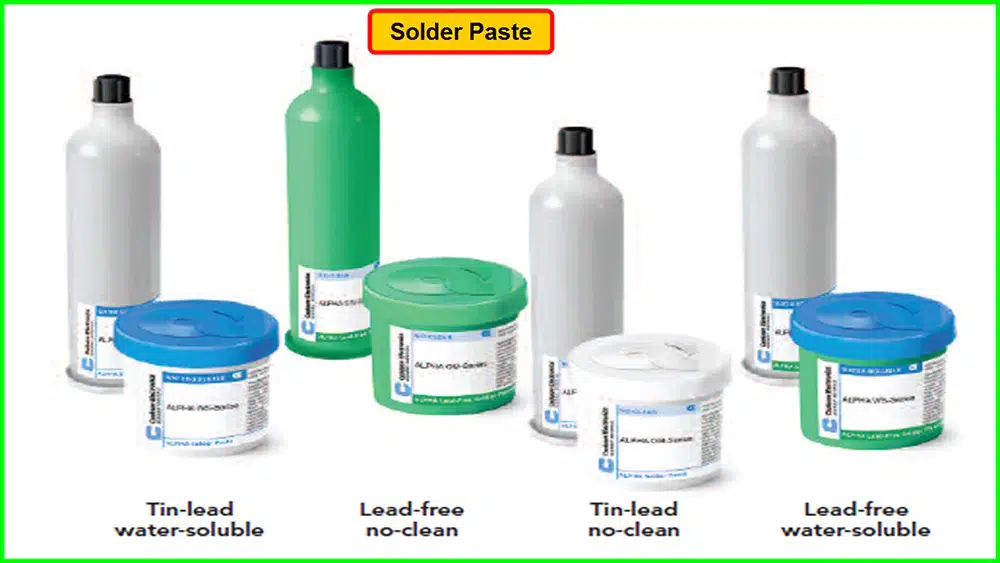

There are several variations of solder paste available. Each of them has special properties and modes of application. Here are the most commonly used solder paste types:
Water-soluble solder paste is required for particular uses. Find out if yours does need this type.
Certain assemblies cannot withstand the extremely high temperatures required for lead-free soldering. Low-temperature solder paste will be effective in these circumstances.
A successful and good assembly depends on both reliability and cost-factor. For higher production efficiencies and revenue, a high-reliability solder paste is appropriate.
The majority of manufacturers are converting to no-clean alternatives from water-soluble solder pastes. This is in a bid to get rid of the water wash procedure.
Those who participate in private endeavors can utilize leaded solder pastes based on the elevated melting point. You need lesser heat when using leaded solder paste. This makes them the best choice for one-off projects.
Items must be created using lead-free materials because of RoHS limits and requirements. Lead pollution is rapidly on the rise throughout landfills all over the globe. Therefore, sustainability in manufacturing is imperative.
Metallic solder alloy and a flux carrier are combined to make solder paste. The metallic solder alloy is constructed of lead, tin, and other metals like copper and silver, whereas the flux vehicle is composed of organic compounds. The two come together to make a paste that bonds components to the surface of the PCB.
The application of the paste will highly determine its composition. What elements are in the solder paste might also depend on the specific demands of the soldering procedure. Typically, the flex vehicle makes up 10-20% of the composition, while the metal solder alloy makes up about 80-90% of the composition.
The purpose of the flux vehicle is to clean up the surface of the components that are joined together. It also prevents oxidation and contaminants from affecting the entire soldering procedure. Additionally, it regulates the solder paste’s flowing and hydration throughout the reflow process. The solder becomes stronger and creates reliable bonds.
Throughout board assembly, a substance called solder paste is put into printed circuit boards. It links electronic components to the board. The application process utilizes a dispenser or stencil. The solder particles are then melted out of the paste, creating a strong, long-lasting link between the circuit board and its parts.

The majority of today’s devices are typically assembled using SMT, which is suited for solder paste.
Utilizing solder paste for SMD assembly ensures that the process is not only faster, but also efficient when compared to conventional through-hole assembly procedures. In fact, it even allows for the formation of minute and more sophisticated electronic devices.
Frequently, many individuals believe that solder paste and solder wire have the same meaning. Both are distinct forms of solder that join metal surfaces together. The mode of application and physical forms make up the main differences between the two.
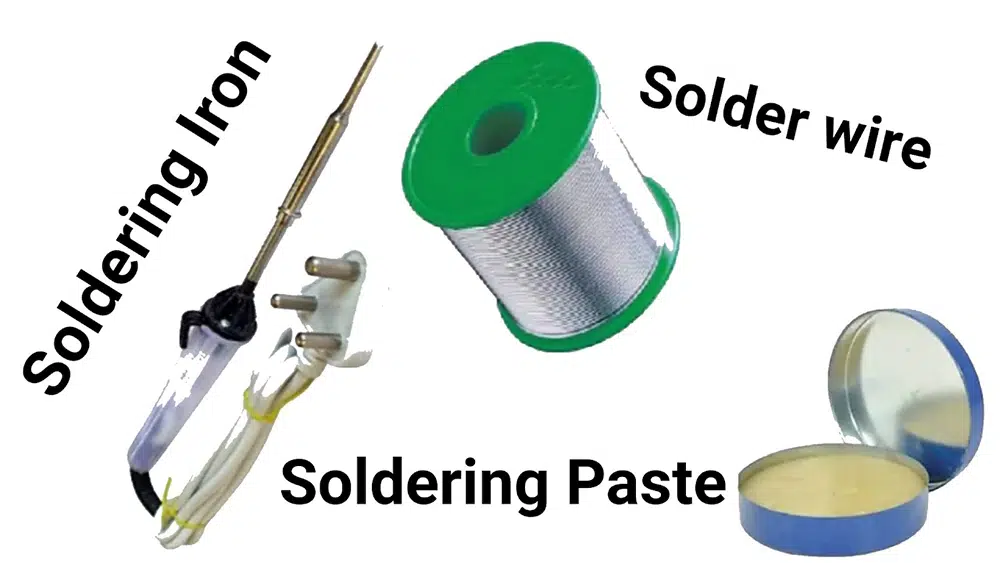

Solder wire is a spool of thin wire from metal alloys that melt at very low temperatures. It is ideal for hand soldering. The wire gets heat from a soldering iron and is then applied to the joint.
On the other hand, solder paste is a paste-like material that is employed in reflow soldering and is identified by its name. This paste is applied to a PCB’s face and heated in an oven to melt the solder and attach the parts.
Several variables, including as the substrate material, the kind of elements being soldered, and the assembly procedure, will determine the best solder paste to employ in any specific application.
As shown above, there are various varieties of solder paste accessible. Each one has its unique form and characteristics.
Depending on how much solder paste you need, you can get it from your local hardware store or via a wholesale supplier/manufacturer like IBE. Talk to us today and discover the many options that we have on the table for your selection.