Electrical short circuit is a frequent problem that can harm equipment, start fires, and even endanger people’s safety. A thorough grasp of short circuits, their causes, and how to spot and avoid them is crucial. We examine frequently asked inquiries concerning short circuits in this article.
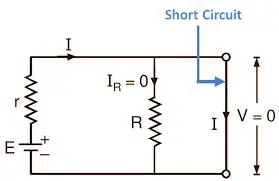
A short circuit is an electrical issue that happens when two points in an electrical circuit accidentally form a low-resistance channel to one another. Through this route, the typical load or resistance is bypassed, allowing for a significant electrical current flow. A short circuit can therefore result in an excessive current flow, overheating, damage to the equipment, and even constitute a fire risk.
There are primarily three types of short circuits:
● Line-to-Line Short Circuit: When two conductors with different phases come into direct contact, bypassing the load, a short circuit of this sort happens. Typically, a mechanical malfunction or an insulating flaw cause it.
● Line-to-Ground Short Circuit: Here, one or more conductors make touch with a grounded object or the ground. It may be brought on by deteriorating insulation, frayed wires, or defective machinery.
● Double Line-to-Ground Short Circuit: This kind includes the simultaneous contact of two conductors with the ground or grounded components. It is the most severe kind of short circuit and frequently results from a phase-to-phase fault that then contacts the ground or a fault involving many phases.
Some properties of a short circuit include:
● Low electrical resistance: In comparison to normal operating circumstances, a short circuit offers a route of least resistance for current flow, leading to a much higher current flow.
● High current flow: A short circuit results in an increase in current that is only constrained by the impedance of the power source and the components of the circuit.
● Voltage drop: Because the bulk of the supply voltage is lost across the shorted channel, a short circuit can cause a sizable reduction in voltage across the circuit.
● Excessive heat generation: The high current travelling through the short circuit may cause nearby materials to become overheated, perhaps resulting in damage or fir.
Short circuits can occur due to various reasons, including:
● Insulation failure: A short circuit may result through contact between conductors or between conductors and ground as a result of the degradation, damage, or deterioration of insulating materials. A short circuit may result through contact between conductors or between conductors and ground as a result of the degradation, damage, or deterioration of insulating materials.
● Faulty wiring or connections: Damaged wires, improper connections, or shoddy wiring can direct electricity in unanticipated directions.
● Equipment failure: Short circuits can be brought on by malfunctioning or broken electrical devices like switches, outlets, or appliances.
● Overloading: A short circuit might happen if you overload a circuit with more electricity than it can handle. This can cause heat.
● Environmental factors: Short circuits can result from insulation integrity being compromised by external sources such moisture, dust, or pollutants.
Also read: How does the residue impact PCBA reliability?
During a short circuit, a sudden surge of current flows through an unintended low-resistance path. This high current can cause several effects, such as:
● Voltage drop: Due to the low resistance, the voltage across the shorted component of the circuit reduces dramatically, while the voltage across the remaining portion of the circuit may increase.
● Overheating: Heat produced by the high current might quickly accumulate in the conductors, parts, or surrounding materials and cause damage or a fire.
● Circuit protection activation: Circuit breakers or fuses respond to the excessive current by detecting the irregularity and swiftly interrupting the circuit to stop additional harm.
Identifying a short circuit typically involves the following steps:
● Visual inspection: Check the circuit for any obvious evidence of damage, such as scorched wires, melted or burned insulation, or blackened components.
● Circuit isolation: By shutting off the associated breaker or disconnecting the fuse, you may separate the power supply from the circuit. This guarantees safety while doing the check.
● Continuity testing: To look for a low-resistance route between two sites, use a multimeter in the continuity or resistance mode. A short circuit may exist if the metre displays continuity or a very low resistance value.
● Insulation resistance test: Use a megohmmeter to gauge the insulation resistance between the conductors and between the conductors and ground while the circuit is still isolated. A probable short circuit is indicated by a considerably low insulation resistance value.
● Thermal imaging: Hotspots brought on by an overabundance of heat produced in the shorted area can be found using infrared thermography. This technique is very helpful for finding concealed short circuits inside of machinery or behind walls.
● Professional assistance: It’s suggested that you seek assistance from a certified electrician or technician who can use specialised tools and methods for precise diagnosis if you’re unclear or unable to recognise the short circuit.

There are numerous steps that may be done to avoid short circuits. In order to safeguard electrical conductors and cables from physical harm, moisture, and pollutants, appropriate insulation is first and foremost necessary.
Second, utilising electrical equipment that is dependable, certified, and compliant with safety requirements, as well as having it regularly maintained and inspected, will assist prevent short circuits.
Third, it’s important to follow the right wiring procedures, which include the right wire size, safe connections, and avoiding excessive bundling or overloading of circuits. By implementing efficient earthing and grounding systems, you may avoid line-to-ground short circuits and provide electrical faults a safe channel to go.
Furthermore, installing the proper safety equipment, such as circuit breakers, electronic fuses, or ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), aids in the prompt detection and interruption of faults or high currents. Regularly checking, testing, and maintaining electrical systems can find possible problems and fix them before they become short circuits.
Last but not least, it’s critical to make sure that those who work with electrical systems are properly trained in electrical safety procedures and are aware of the dangers of short circuits.

Short-circuit current calculations take the impedance of the system and the available fault current from the power supply into account. The precise computation is based on the electrical system’s unique properties and the fault situations. The values of the system’s impedance, the fault current contributions from various sources, and the network design are often needed for an extensive computation. Using software tools created expressly for short-circuit analysis, such as power system analysis software, it is a difficult operation that is frequently carried out by electrical engineers or specialists.