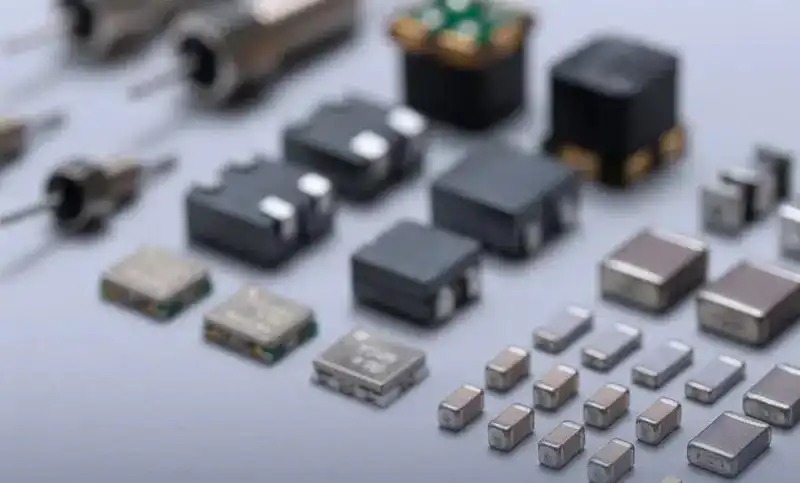

In today is fast-paced electronic world, Surface Mount Device (SMD) components are playing a vital role in making our devices smarter, smaller, and more efficient. These tiny yet powerful components have revolutionized the way we build and use electronics, enabling us to cram more functionality into less space while still achieving high levels of performance. It’s safe to say that SMD components have become an indispensable part of modern electronic devices, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
These components have revolutionized the electronics industry and have allowed manufacturers to produce smaller, more lightweight, and more sophisticated devices. This article will provide an overview of SMD components, including their types, identification, assembling process, defects, testing, and the difference between SMT and SMD.
SMD components have become the darlings of the electronics world, thanks to their unique design and high-performance capabilities. These tiny electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB, offering a more efficient and reliable alternative to through-hole components. Unlike their bulkier through-hole counterparts, SMD components are designed to be soldered in place using a reflow process, allowing for greater precision and control during manufacturing. This process enables SMD components to be much smaller in size, while still delivering superior performance and reliability, making them the go-to choice for modern electronics designers.
The world of SMD components is diverse and dynamic, with a wide variety of components to choose from, each with its own unique features and applications. From PCB capacitors and resistors to PCB diodes and transistors, SMD components come in many shapes and sizes, making them ideal for a wide range of electronic applications.
Resistors are rectangular-shaped components that help regulate the flow of current in a circuit and are available in both thin-film and thick-film variants. On the other hand, SMD capacitors are used to store electrical charge and come in different types such as tantalum, ceramic, and electrolytic capacitors.
Diodes, another type of SMD component, are used to allow electrical current to flow in a single direction, and are commonly employed in rectifier circuits. Silicon, germanium, and Schottky diodes are some of the commonly used SMD diodes.
SMD transistors are critical components that can amplify and switch electrical signals, making them indispensable in modern electronics. Bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and field-effect transistors (FET) are some of the different types of SMD transistors available in the market.
Moreover, SMD ICs are the tiny brains that power our modern electronic devices. They’re made up of interconnected components like transistors, diodes, and resistors, and are used in microcontrollers, memory chips, amplifiers, and more. They enable manufacturers to create smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient devices, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in electronics.
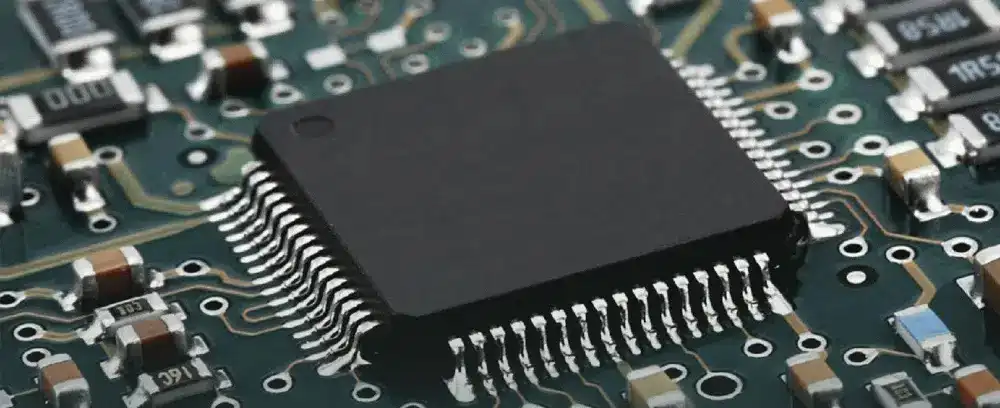

Initially, identifying SMD components can seem like a daunting task. But fear not! There are several ways to identify these tiny components, including looking for component markings, understanding package styles, and comparing their size to other components.
Most SMD components are marked with a code that gives information about their type, value, and tolerance. You can usually find this code on the component’s surface and decode it using a datasheet or online search. Additionally, each package style has its own unique characteristics that can help you identify SMD components quickly.
And, of course, SMD components are typically much smaller than through-hole components, making them easy to spot. By comparing their size to a known reference, you can quickly determine if you’re dealing with an SMD component or not.
With a little practice and knowledge, identifying SMD components will become second nature and help you tackle any electronic project with confidence.
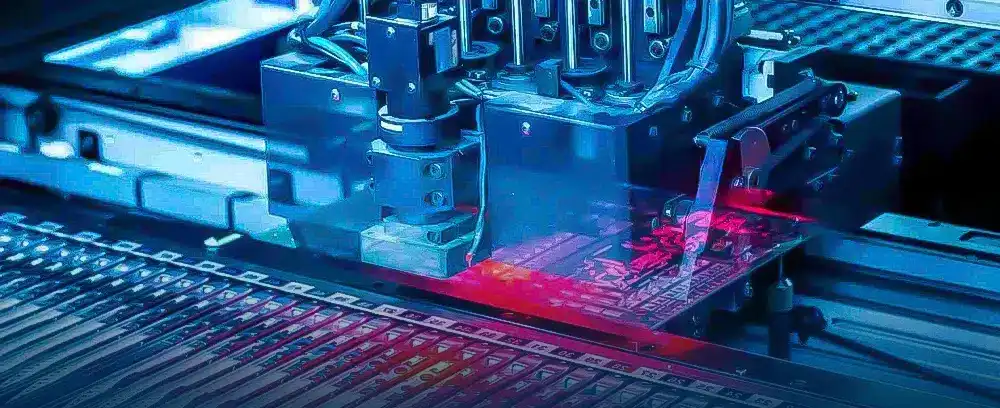
SMD component assembly is a fascinating and intricate process that involves several steps to ensure the proper functioning of electronic devices. Here’s a breakdown of the assembly process:
First, a stencil is used to apply solder paste to the PCB surface. The paste is forced through the openings in the stencil, leaving the pattern of the desired circuit.
Next, the SMD components are carefully placed onto the PCB surface using a pick-and-place machine. The machine uses a vacuum to pick up each component and place it precisely in the correct location on the PCB.
Finally, the entire assembly is heated in a reflow oven, which uses a controlled temperature profile to melt the solder paste and create a permanent connection between the components and the PCB.
It’s a highly precise and intricate process that requires skill and precision, but it’s essential for creating the efficient and reliable electronic devices that we use every day.
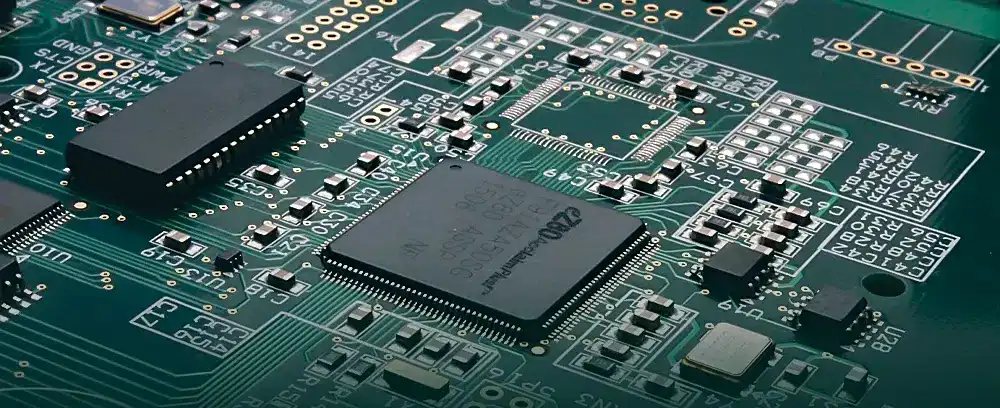
SMD component soldering can be prone to several defects, including:
● Solder Bridging:
Solder bridging occurs when two or more solder joints are connected by a small bridge of solder. This can cause a short circuit and can be difficult to detect.
● Tombstoning:
Tombstoning occurs when one end of an SMD component lifts off the PCB during reflow, causing it to stand upright like a tombstone. This can cause an open circuit and can be caused by uneven heating or incorrect component placement.
● Insufficient Solder:
Insufficient solder occurs when insufficient solder creates a proper connection between the component and the PCB. This can cause a weak or intermittent connection and can be caused by incorrect stencil printing or incorrect component placement.
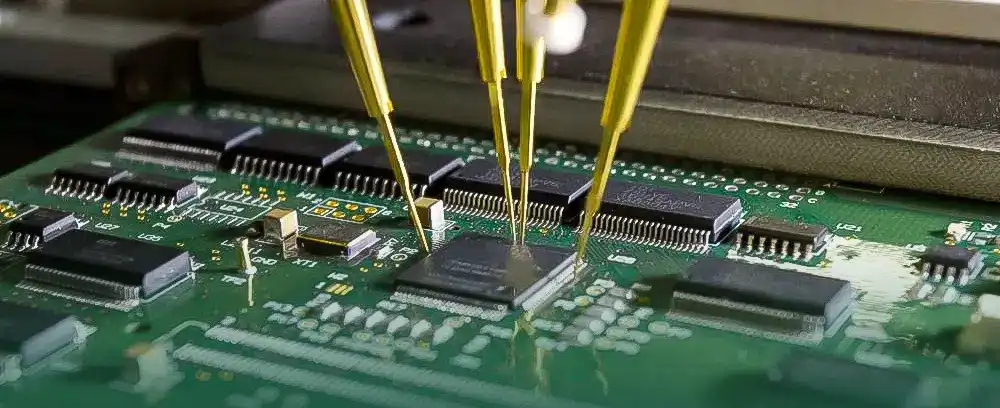
Testing SMD components can be challenging due to their small size and complex circuitry. However, there are several methods that can be used to test these components, including:
● Visual Inspection:
Visual inspection involves examining the component for any visible defects, such as cracks, discoloration, or damage. This can be done using a magnifying glass or microscope.
● Continuity Testing:
Continuity testing involves using a multimeter to test the connection between two points on a circuit. This can be used to check for opens or shorts in SMD components.
● Functionality Testing:
Functionality testing involves testing a circuit’s component to ensure it is functioning correctly. This can be done using specialized equipment, such as a function generator or oscilloscope.
In the world of electronic manufacturing, it’s essential to understand the difference between SMT and SMD. SMT is the process of mounting components directly onto the surface of a PCB, whereas SMD is a type of SMT component that is designed to be mounted onto the PCB surface using a reflow soldering process.
However, it’s important to note that not all SMT components are SMD components. Some SMT components can be mounted using other techniques, such as press-fit or through-hole technology. Knowing the differences between these techniques can help you choose the best components for your specific application and manufacturing process.
So that’s about everything you need to know about integrated circuits and how they work. We at Qtech are always ready to give you solid advice about PCBs, PCBA, and ICs. Talk to us today and find out more on what we offer. With over a decade of experience in this field, you’re guaranteed quality always.