Although “printed circuit board (PCB)” is the most common term, “printed wiring boards” and “printed wiring cards” are also acceptable alternatives. Before PCBs, electrical circuits had to be built using the time-consuming method of point-to-point wiring. The insulation on the wires deteriorated and caused frequent failures at the connections and short courses. Let us check out the details of what is PCB.

A PCB is a thin board constructed of a non-conductive substance designed to accommodate copper circuitry. Electronic components like transistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and so on may be connected through the printed conductive channels on the board.
Network cards, GPUs, motherboards, and the internal circuitry board of hard drives are all examples of PCBs’ wide range of applications in the computer and electrical device industries. In today’s article, we will cover all the details of what is PCB?
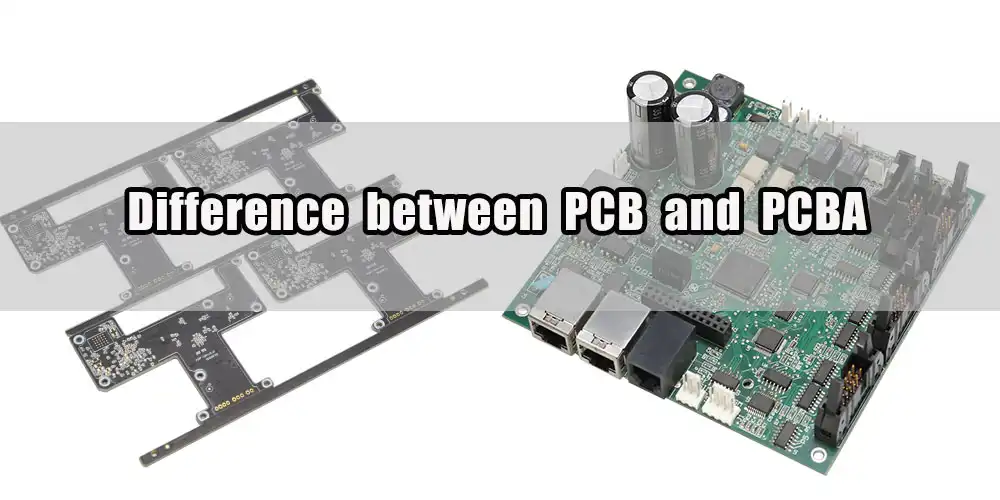
Let’s see what is PCB. Considering all the moving parts and procedures that go into making a PCB, making a blank circuit is the easier option. The process begins with the fabrication of PCBs and progresses to PCBA fabrication.
The packaging of PCBs and PCBAs is another distinction. Vacuum packaging is often used for PCBs. However, PCBAs must be packed in either a compartmentalized or an anti-static environment.

Now, we will see what is PCB made of. PCBs are often fabricated using copper circuit layers on materials other than a substrate. However, there are differences in the way that each PCB type is built. More specifically, PCB may be broken down into a few distinct categories. Here, we will go through the materials used to construct various PCBs and the benefits they provide to help you make an informed decision.
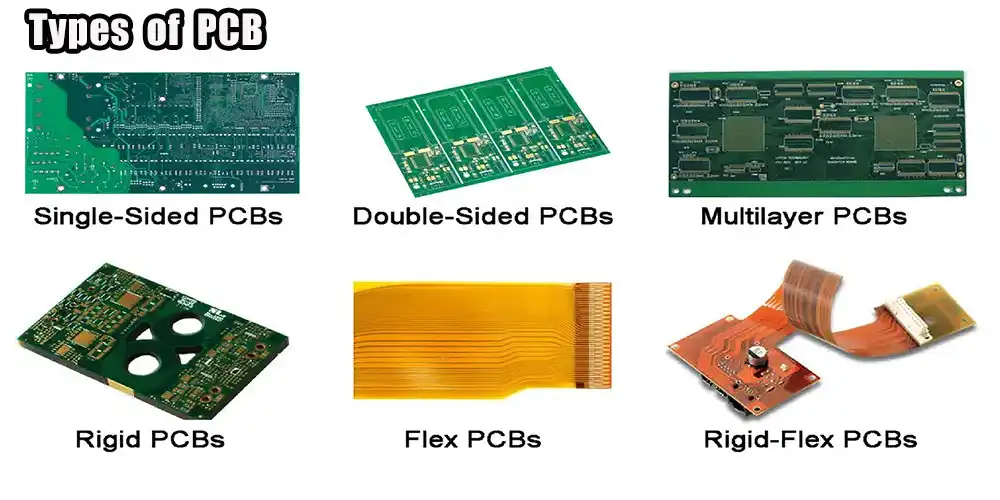
Let’s check what is PCB and the types of PCB. Based on their fabrication methods, design requirements, and end-use industries (such as healthcare, transportation, military, and aerospace), printed circuitry (PCBs) are separated into several subcategories. PCB board varieties are made possible by more sophisticated designs informed by the demands and preferences of customers. Space, stress, and electrical and mechanical stability are just a few factors to consider before settling on a printed circuit board
Typically, PCBs only have one side. Since there is even one conduct layer and no crossing or overlapping is allowed, the conductive paths on these boards need a great deal of space.
We have already discussed what is PCB. A rigid PCB is a flexible circuit board that can’t be bent or twisted. The substrate, or foundation material, is stiff, giving the board its strength and rigidity. Using glue and heat, the various layers—including the substrate, copper, solder mask, and silkscreen—are bonded together to form the finished product. Unlike other circuit boards, Rigid PCBs may be any of these three types, depending on the application. However, alterations are not possible.
A stretchy circuit board is the product of the assembly of several printed circuits and components on a fluid substrate. It is common to practice fabricating flexible PCBs out of the transparent conductive polyester blend, nylon, or PEEK.
These flexible circuit boards are made from the same components as their stiff counterparts. The main distinction is that the board may be used as intended without distorting the shape. There may be one, two, or more layers to these PCBs. Then, the difficulty of a unit installation is reduced.

After you are aware of what is PCB, PCBs are boards used to link various electrical components. They play a crucial role in most electrical devices we use daily. PCB can be founded even in an unimpressive object we use every day such as light. Actually, PCBs are not only employed in home electronic appliances. They can also be used in medical, military, aerospace, consumer electronics and other areas. Here are some areas as follow.
PCB plays a key role in diagnosis, monitoring data related to health situations,s and conducting treatment. For example, infusion pumps, blood pressure monitors, and ultrasonic scanners, pacemakers, and so on.
A variety of consumer electronics can’t be normally operated without PCB. For example, smartphones, computers and home appliances.
In this industry, PCB is usually used to withstand harsh machine operation circumstances like extreme temperatures and chemicals, vibrating machinery. The industrial equipment that has used PCB includes solar power generation devices and electronics power and so on,
Featured with better performance on withstanding extreme temperatures and vibrations, flex-rigid PCB is favored and widely adopted by automobile manufacturers in this area. Here are some instances: stereos and systems, control systems and sensors.
Compared with the automobile, and industrial equipment, aerospace has more strict requirements on PCB. Lightweight materials used on PCBs are crucial for aerospace components. For instance, aircraft, control towers, satellites, pressure sectors, and accelerometers, etc.
Before learning the process know the details of what is PCB. Laminating (heating & pressing) board materials with high temperatures to create the PCB layer stack up. Making holes for screws, pins, and vias to go through while installing. Surface etching, or the removal of excess copper, exposes traces and pads. Filling and plating via pinholes.
Here is a video to show the process of PCB manufacturing.

PCBs are used in many electronic applications; they are flat plates or bases made of insulating materials with patterns of conductive materials and components. However, PCBs all begin in the same place: the design phase.
Time and money are wasted when many costly modifications hold up a project. Consult engineering professionals early on to design for ease of manufacture and guarantee an effective, efficient, and low-cost product. So before starting the design of PCB learn the details of what is PCB.